Coupling Flows
- Consider a continuous random variable z∈RD
- Partition z into two subsets : eg two contiguous sub-vectors using a function g
- Open: Pasted image 20241119165521.png
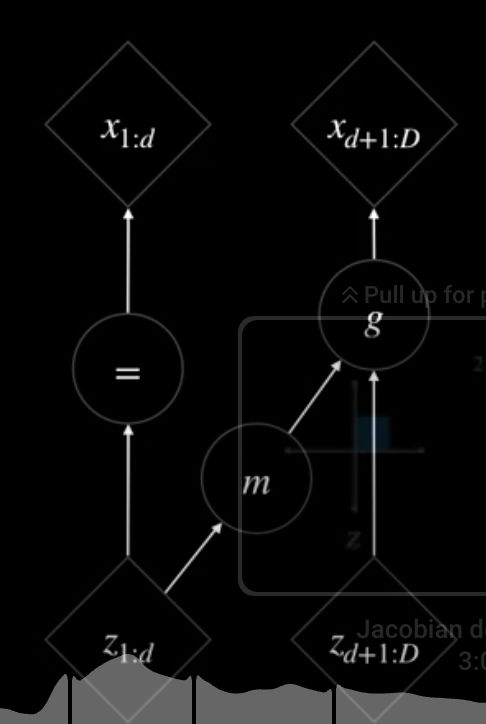
- \begin{align*} x_{1:d}= z_{1:d} \\ x_{d+1:D}= g(z_{d+1:D}; m(z_{1:d})) \end{align*}
- elements in the first subset are not affected by those in the second
- to invert them is trivial \begin{align*} z_{1:d}= x_{1:d} \\ z_{d+1:D}= g^{-1}(x_{d+1:D}; m(x_{1:d})) \end{align*}
- Additive coupling layer
- Scaling matrix for coupling layers
