RANSAC
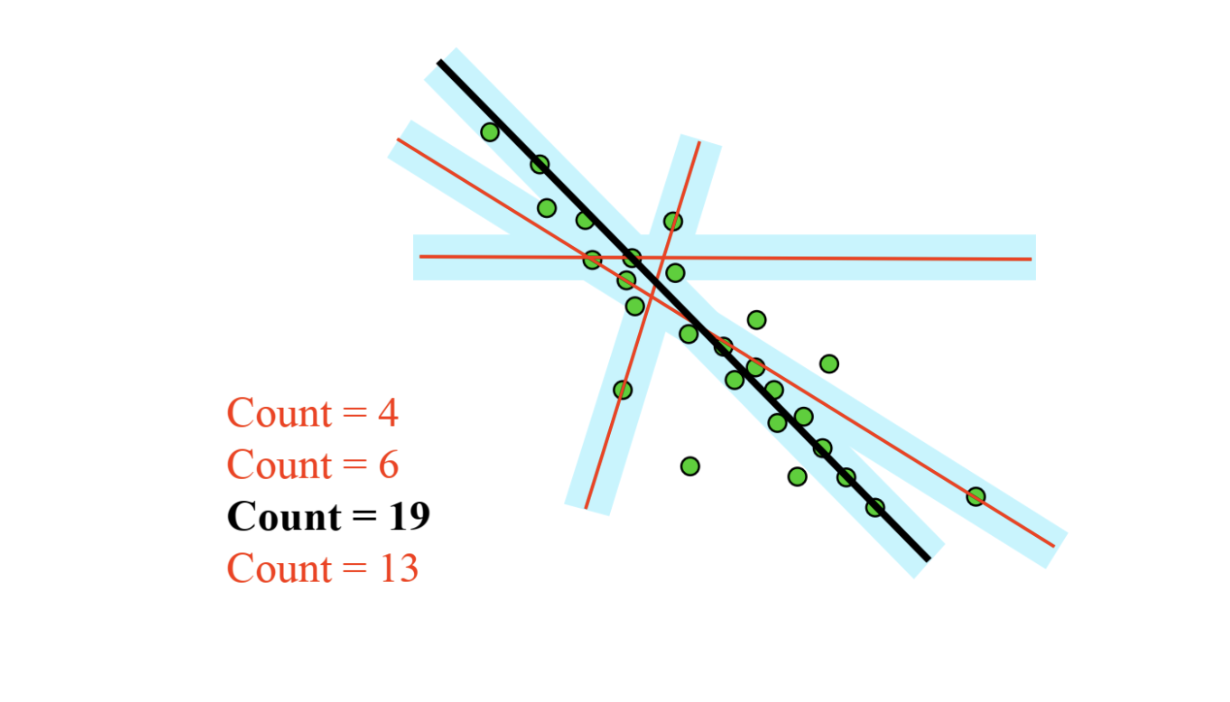
- It is an iterative method to estimate parameters of a mathematical model from a set of observed data
- A simple example is fitting a line to a set of observations.
- Outliers are points that don’t “fit” the model and points that do fit are called “inliers”
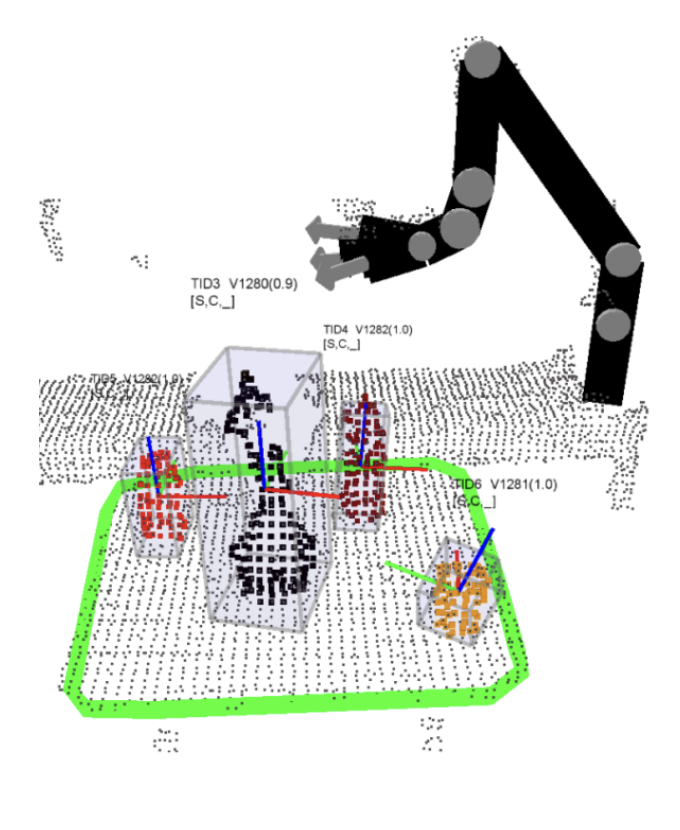
- Table detection
- The algorithm starts by generating plane hypotheses based on three unique points.
- For each plane hypothesis, distances from all points in the point cloud to the plane are computed.
- The plane hypotheses are then scored based on counting the number of inlier points, e.g., distance to the plane 20mm.
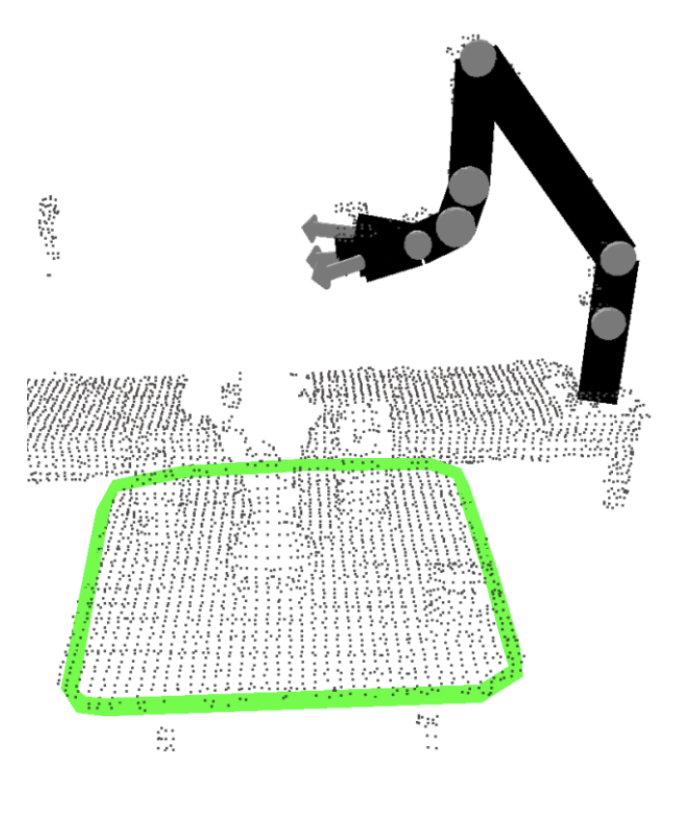
- The RANSAC algorithm is repeated for a certain number of iterations, e.g., n = 200.
- Object detection
- It is now possible to extract the points which lie directly above it.
- By removing the table, we have a point cloud where all the objects that are on top of the table are included.
- The obtained point cloud is then segmented into individual clusters Each small group of points will be treated as an object candidate.