Biological Neuron
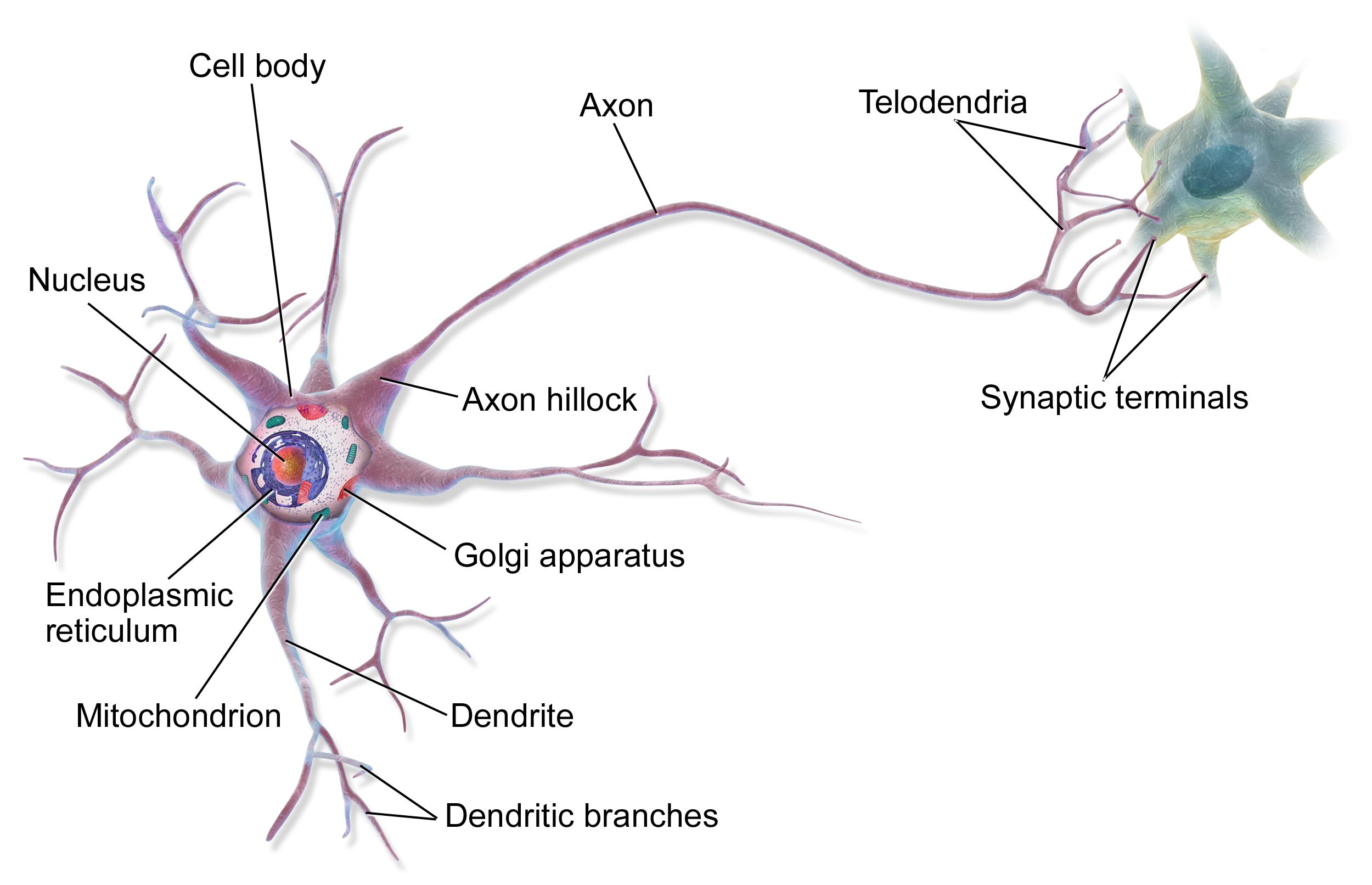
- (from)
- composed of
- cell body
- Dendrites: many branching extensions
- Axon: very long extension that splits off at its tip into many branches called synaptic terminals
- composed in a network (e.g. brain) by synaptic terminals of one neuron connected to Dendrites of other neurons
- electrical impulses (signals) are sent from other neurons via these synapses
- if a neuron receives a sufficient number of signal from other neurons within a few milliseconds, it is exited and fires its own signals (activation)
- connectivity in a biological neural system is huge, human brain:
- number of neurons: ≈1011
- number of connections per neuron: ≈104
- networks are organized into hierarchical structures
- Irreplacable
- Requires constant supply of Glucose
